resultant of vector formula|Iba pa : Tagatay Learn how to calculate the resultant vector using the head to tail method and the parallelogram method. See examples, diagrams, formulas and practice problems for . Eyes on Fire: Directed by Mac Alejandre. With Sid Lucero, Paolo Gumabao, Angeli Khang, Dexter Doria. Take a peek at the life of an unhappy housewife who finds passionate love from her neighbor and how their affair brings them closer to fire.
resultant of vector formula,Find out how to use the resultant vector formula to compute the resultant of two or more vectors in different directions. See solved examples and learn how Sherlock applied this formula to solve a .Learn how to calculate the resultant vector of two vectors using the formula \\ [\\large \\overrightarrow {R}=\\sqrt {\\overrightarrow {x^ {2}}+\\overrightarrow {y^ {2}}}\\] . .
Learn how to find the resultant vector of two or more vectors using different formulas depending on their orientation. See solved examples with step-by-step .
Learn how to calculate the resultant vector of two or more vectors based on their direction and magnitude. See examples, formulas and applications in engineeri.Learn how to calculate the resultant vector using the head to tail method and the parallelogram method. See examples, diagrams, formulas and practice problems for .

Learn what a resultant vector is, how to find it using geometric or analytical methods, and how to draw it using the head-to-tail rule or the parallelogram law. See examples of adding two or more vectors and .The resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the .
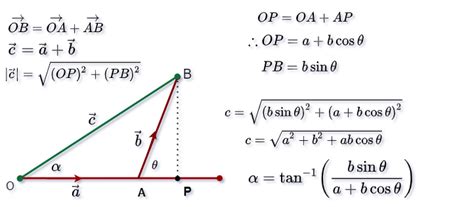
The formula for finding the resultant vector when vectors are inclined to each other is: R 2 =A 2 +B 2 +2AB×cosØ, where A and B are the magnitudes and Ø is the .For vectors represented by their magnitude (size) and direction (angle) relative to a reference axis, you can calculate the resultant vector using these formulas: Resultant .resultant of vector formula Iba paFormula 1. To get the resultant vector, simply combine vectors in almost the same direction. P and Q are the same-direction vectors, while A is the resulting vector. P + Q .
Step 1. Draw the diagram of showing angle of resultant vector: Let P and Q be two vectors acting at the same instant at a point and represented both in magnitude and direction by two adjacent sides O A and O D of .

Hence, the resultant vector is \((15, 16, 4)\). Uses of Resultant Vectors. Resultant vectors are widely used in physics to represent multiple forces acting on an object as a single equivalent force. This simplification is essential for understanding the overall effect and for performing calculations more efficiently. From determining the net .The resultant vector is known as the composition of a vector. There are a few conditions that are applicable for any vector addition, they are: . The above equation is the magnitude of the resultant vector. To .vector sum of two (or more) vectors. scalar. a number, synonymous with a scalar quantity in physics. scalar component. a number that multiplies a unit vector in a vector component of a vector. scalar equation. equation in which the left-hand and right-hand sides are numbers. scalar product.resultant of vector formulaThe analytical method of vector addition involves determining all the components of the vectors that are to be added. Then the components that lie along the x-axis are added or combined to produce a x-sum. The same is done for y-components to produce the y-sum. These two sums are then added and the magnitude and direction of the resultant is .Consider two vectors P and Q with an angle θ between them. The sum of vectors P and Q is given by the vector R, the resultant sum vector using the parallelogram law of vector addition.If the resultant vector R makes an angle β with the vector P, then the formulas for its magnitude and direction are: |R| = √(P 2 + Q 2 + 2PQ cos θ); β = tan-1 [(Q sin .
The standard unit vectors extend easily into three dimensions as well, ˆi = 1, 0, 0 , ˆj = 0, 1, 0 , and ˆk = 0, 0, 1 , and we use them in the same way we used the standard unit vectors in two dimensions. Thus, we can represent a vector in ℝ3 in the following ways: ⇀ v = x, y, z = xˆi + yˆj + zˆk.Let P and Q be two vectors acting simultaneously at a point and represented both in magnitude and direction by two adjacent sides OA and OD of a parallelogram OABD as shown in figure. Let θ be the angle between P and Q and R be the resultant vector. Then, according to parallelogram law of vector addition, diagonal OB represents the resultant .
resultant of vector formula|Iba pa
PH0 · vector addition resultant formula
PH1 · resultant vector formula with angle
PH2 · resultant of two vectors
PH3 · resultant of a vector
PH4 · magnitude of resultant vector formula
PH5 · formula to find resultant vector
PH6 · direction of resultant vector formula
PH7 · angle of resultant vector
PH8 · Iba pa